Section 3.5
Oil Pump and Sump Pipe
In the EPA 04 (EGR) engine, there are minor changes to the oil pump. The EGR engine has a higher oil output now. There are larger internal gears compared to the EPA 98 (non-EGR) version which has smaller internal gears. See Figure "Comparison on Oil Pump Internal Gears" .
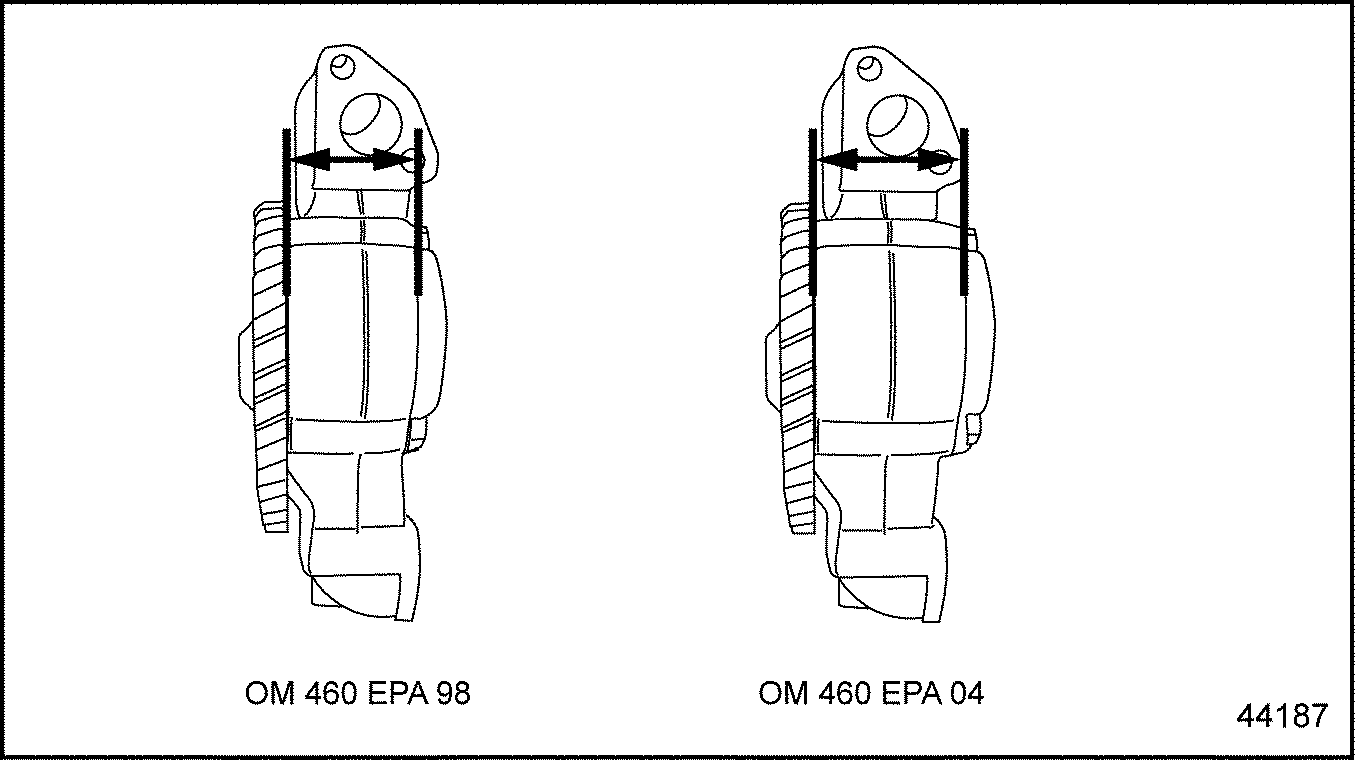
Figure 1. Comparison on Oil Pump Internal Gears
The mounting point location on the EGR engine oil sump pipe is 3.0 mm (0.118 in.) longer in length than the non-EGR sump pipe. The removal and installation procedures are the same for the non-EGR and EGR engine. See Figure "Oil Pick Up Tube in the EPA 04 (EGR) Engine" .

Figure 2. Oil Pick Up Tube in the EPA 04 (EGR) Engine
Perform the following procedures for removal of the oil pump.
Section 3.5.1
Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Removal
Remove the oil pump assembly as follows:
- Remove the oil pan from the cylinder block. Refer to "3.2.1 Oil Pan Removal" .
- Remove the sump pipe from the oil pump. See Figure
"Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Removal"
.
- Remove the bolt attaching the sump pipe bracket to the cylinder block.
- Remove the two bolts attaching the sump pipe to the oil pump. Discard the gasket.
- Remove the sump pipe and bracket from the oil pump.
- Remove the bolts attaching the pressure limiting valve to the oil pump and lower edge of the cylinder block. Remove the pressure limiting valve from the oil pump. See Figure
"Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Removal"
.

1. Valve Mounting Bolt
6. Sump Pipe Mounting Bolt
2. Pressure Limiting Valve
7. Sump Pipe
3. Oil Pump
8. Bracket
4. Oil Pump Mounting Bolt
9. Bracket Mounting Bolt
5. Gasket
Figure 3. Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Removal
- Remove the bolt attaching the oil pump to the cylinder block. Remove the oil pump from the the cylinder block. See Figure "Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Removal" .
- Thoroughly clean the contact surfaces of the oil pump and cylinder block.
Section 3.5.2
Oil Pump Disassembly
Disassemble the oil pump unit as follows:
- Remove the oil pump from the cylinder block. Refer to "3.5.1 Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Removal" .
- Remove the face plate mounting bolts and remove the face plate from the oil pump housing. See Figure
"Oil Pump (exploded view)"
.

1. Face Plate Mounting Bolt
4. Pump Drive Gear
2. Face Plate
5. Pump Housing
3. Idler Gear
6. Drive Wheel
Figure 4. Oil Pump (exploded view)
- Remove the idler gear from the pump housing.
- Using an appropriate drift, press the drive wheel off the pump drive gear.
- Remove the pump drive gear from the pump housing.
- Inspect the idler gear, pump drive gear, face plate, and pump housing for damage and excessive wear. Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Note: If either the idler gear or pump drive gear needs replacing, replace both gears as a set.
- Check the idler and pump drive gears. Check their seats in the pump housing and face plate. Listed in Table
"Oil Pump Inspection Limits"
are the acceptable limits.
Description
mm (in.)
Diameter of Shaft Bore (in pump housing and face plate)
22.000-22.021 (0.8661-0.8670)
Diameter of Idler Gear and Pump Drive Gear Shaft
21.93-21.94 (0.8634-0.8638)
Clearance of Pump/Idler Gear to Walls of Pump Housing
0.030-0.122 (0.0012-0.0048)
Gear Backlash (clearance between gear cogs)
0.312-0.476 (0.0123-0.0187)
Table 3. Oil Pump Inspection Limits- In the pump housing, measure the diameter of both gear shaft bores, the idler gear seat and the pump drive gear seat. If the measurements are not within acceptable limits, replace the pump housing.
- Measure the diameter of both shaft bores in the face plate. If the measurements are not within acceptable limits, replace the face plate.
- Measure the diameter of the pump drive gear shaft and the idler gear shaft. If the measurements are not within acceptable limits, replace both gears as a set.
- Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the gears and the pump housing wall. If the measurements are not within acceptable limits, replace both gears as a set.
- Using a feeler gauge, measure gear backlash (the clearance between two adjacent cogs on different gears). If the measurements are not within acceptable limits, replace both gears as a set.
Section 3.5.3
Oil Pump Assembly
Assemble the oil pump unit as follows:
|
BURNS |
|
To avoid injury from burning, use lifting tools and heat-resistant gloves when handling heated components. |
- Heat the drive wheel to approximately 80°C (176°F) in a hot water tank.
- Seat the pump drive gear in the pump housing. Using an appropriate drift, press in the heated drive wheel until the pump drive gear projects slightly past the top of the drive wheel. See Figure
"Positioning the Drive Wheel on the Pump Drive Gear"
.

1. Pump Drive Gear
2. Drive Wheel
Figure 5. Positioning the Drive Wheel on the Pump Drive Gear
- Using a feeler gauge, measure the projection of the pump drive gear. Adjust the position of the pump drive gear until the projection equals 0.5 mm (0.02 in.), as listed in Table
"Oil Pump Installation Specifications"
.
Description
mm (in.)
Projection of Pump Drive Gear
0.5 (0.02)
Pump/Idler Gear End Play
0.050-0.128 (0.0020-0.0050)
Table 6. Oil Pump Installation Specifications - Seat the idler gear in the pump housing.
- Install the face plate on the pump housing. Tighten the mounting bolts to 25 N·m (18 lb·ft).
- Using a dial gauge, measure the end play of the pump drive gear and idler gear against the walls of the pump housing. See Figure
"Measuring the Clearance of the Pump Drive Gears"
for set-up and listed in Table
"Oil Pump Installation Specifications"
are the specifications.

1. Dial Gauge
3. Oil Pump
2. Support
Figure 6. Measuring the Clearance of the Pump Drive Gears
- Secure the assembled oil pump in a vise, with the face plate pointing up.
- Rest the dial gauge support on the face plate.
- Set up the dial gauge so that the feeler on the end of the gauge touches the exposed end of the pump drive gear with some preload.
- Force the pump drive gear downward as far as it will go.
- At this position, adjust the scale of the dial gauge to "0" (zero).
- Now force the pump drive gear upward as far as it will go. Read the measurement on the dial gauge and make sure it conforms to the range listed in Table "Oil Pump Installation Specifications" . Replace the pump, if necessary.
- Repeat this procedure for the idler gear.
- Install the oil pump in the cylinder block. Refer to "3.5.4 Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Installation" .
Section 3.5.4
Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Installation
Install the oil pump and Sump Pipe as follows:
- Coat the contact surface between the block and the oil pump with Loctite® 574.
- Position the oil pump on the cylinder block. Make sure the teeth on the drive wheel of the oil pump mesh with the teeth of the crankshaft drive gear. Tighten the oil pump mounting bolt to 35 N·m (26 lb·ft). See Figure
"Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Installation"
.

1. Valve Mounting Bolt
6. Sump Pipe Mounting Bolt
2. Pressure Limiting Valve
7. Sump Pipe
3. Oil Pump
8. Bracket
4. Oil Pump Mounting Bolt
9. Bracket Mounting Bolt
5. Gasket
Figure 7. Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Installation
Note: It may be necessary to rock the pump counterclockwise so the teeth of the drive wheel can properly align with the crankshaft drive gear.
- Check the backlash between the oil pump drive and the crankshaft gear. The specification is 0.077 – 0.333 mm (0.003 – 0.013 in.).
- Install the pressure limiting valve on the oil pump. Tighten the valve mounting bolt to 35 N·m (26 lb·ft).
- Install the sump pipe to the oil pump. Tighten all mounting bolts to 25 N·m (18 lb·ft). See Figure
"Oil Pump and Sump Pipe Installation"
.
- Install the sump pipe bracket on the cylinder block.
- Install the sump pipe, with a new gasket, on the oil pump.
- Install the oil pan with a new gasket. Refer to "3.2.2 Oil Pan Installation" .
- Fill the engine oil circuit. The correct oil fill capacity is listed in Table
"Lubricating Oil Capacity"
.

PERSONAL INJURY
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
- Always start and operate an engine in a well ventilated area.
- If operating an engine in an enclosed area, vent the exhaust to the outside.
- Do not modify or tamper with the exhaust system or emission control system.
- Start the engine and check for leaks.
- Check the engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
| MBE 4000 Service Manual - 6SE412 |
| Generated on 10-13-2008 |